Rockbreakers are indispensable tools in modern mining operations, designed to handle tough materials like boulders, ores, and concrete blocks. These machines enhance productivity by clearing blockages at crusher feeds, screens, and conveyor belts. In this article, we’ll dive deep into how rockbreakers work, explore their types, applications, and selection criteria, and highlight advanced systems like the Rockbreaker Boom System tailored for mining efficiency.
A rock breaker, also called a hydraulic hammer or rock hammer, is a heavy-duty attachment mounted on excavators or stationary booms. It uses high-impact energy to fracture hard materials. Unlike traditional blasting, rockbreakers offer precision, safety, and reduced environmental impact, making them ideal for confined mining spaces.
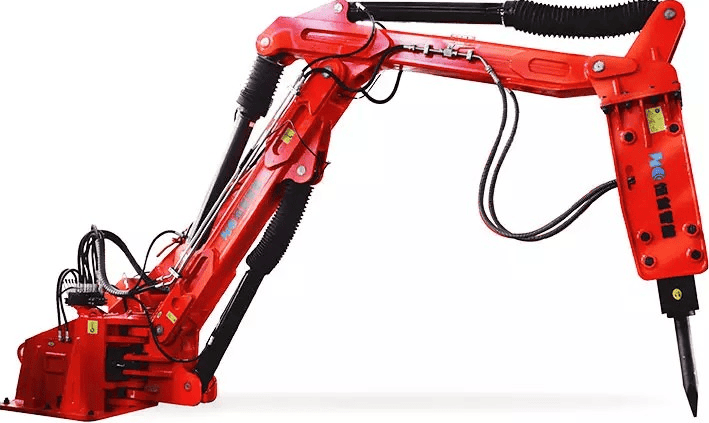
Hydraulic Power Unit (HPU): Generates pressurized fluid to drive the piston.
Boom and Arm Assembly: Positions the breaker tool precisely over the target.
Tool Attachment (Chisel or Moil Point): Transfers impact energy to the rock.
Pressure Generation: The HPU pumps hydraulic oil into the breaker’s chamber.
Piston Activation: Pressurized oil forces the piston upward, compressing nitrogen gas in the accumulator.
Impact Delivery: The piston accelerates downward, striking the tool with kinetic energy (up to 5,000 blows per minute).
Energy Transfer: The tool transmits force to the rock, creating fractures.
Impact Energy: Measured in joules (J) or foot-pounds (ft-lb). Higher energy suits harder rocks.
Blow Rate: Faster cycles improve efficiency but may reduce per-blow force.
Tool Design: Chisels for splitting, moil points for concentrated impact.
Most common in mining due to high power-to-weight ratios. Ideal for primary crushing stations and underground operations.
Use compressed air for lighter tasks like secondary breaking. Less efficient but lower-cost.
Rare in modern mines; rely on mechanical linkages for impact.
| Type | Power Source | Impact Energy (J) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic | Hydraulic Oil | 500–15,000+ | Primary crushing, tunneling |
| Pneumatic | Compressed Air | 100–2,000 | Secondary breaking, demolition |
| Mechanical | Engine-driven | 200–1,500 | Obsolete in most mines |
Soft limestone: Lower energy (500–1,500 J).
Granite/basalt: High-energy breakers (3,000+ J).
Match breaker weight and flow rate to the excavator’s capacity.
Heavy-Duty: Continuous operation (e.g., quarries).
Medium-Duty: Intermittent use (e.g., tunnel maintenance).
| Parameter | Light-Duty | Medium-Duty | Heavy-Duty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Energy (J) | 500–1,500 | 1,500–3,000 | 3,000–15,000 |
| Operating Pressure (bar) | 150–180 | 180–220 | 220–250 |
| Carrier Weight (tons) | 1–10 | 10–30 | 30–100+ |
A Rockbreaker Boom System integrates a hydraulic breaker with an articulating boom, enabling remote operation in hazardous zones. These systems excel at clearing blockages in crushers, screens, and hoppers.
Safety: Operators work from a protected cabin.
Precision: Boom articulation targets hard-to-reach blockages.
Versatility: Combine crushing, clamping, and grading functions.
Check hydraulic lines for leaks.
Monitor tool wear (replace at 30% wear to avoid damage).
Use high-quality hydraulic oil (ISO VG 46 or similar).
Ensure cooling systems prevent overheating.
Rockbreaker: Focuses on pre-crushing blockage clearance.
Rock Crusher: Reduces rock size via compression or impact.
Paving breakers are smaller, air-powered tools for asphalt, while hydraulic breakers handle heavy mining tasks.
From underground tunnels to open-pit mines, rockbreakers streamline material handling while minimizing downtime. Choosing the right breaker—whether a standalone hydraulic hammer or a sophisticated Rockbreaker Boom System—requires evaluating material hardness, carrier compatibility, and duty cycles.
For mines seeking cutting-edge solutions, the Rockbreaker Boom System by HCROT offers unmatched reliability and multifunctionality. Visit www.hcrot.com to explore their range of rockbreaking technologies engineered for the toughest mining challenges.